Do you know how to Dispose of electrical waste can? Statistically speaking, every inhabitant of Germany produces 22.8 kg of electronic waste every year. However, many people make big mistakes when disposing of electrical appliances. Here you will find an overview of the topic of e-waste, including a clear infographic, and learn where and how you can dispose of e-waste correctly.
Here is another short Table of contents about the article:
- Definition
- Facts & Figures
- Dispose of electronic waste correctly
- Electrical appliances to the residual waste?
- Electrical Act
- Costs
- Recycling
- Avoid electronic waste
- Summary & infographic
What exactly is e-waste?
When you think of e-waste, the first thing that probably comes to mind is your old washing machine or your old refrigerator. However, e-waste does not only include these large old appliances, but much more. In general, according to the Electrical and Electronic Equipment Act (ElektroG), electrical waste includes all electrical and electronic...
- ... which depend on electronic currents or electromagnetic fields for their proper operation, or
- ... serve the generation, transmission and measurement of electric currents and electromagnetic fields.
Here is an overview of what is thus considered e-waste, for example:
- Major electrical appliances such as washing machine, dryer, dishwasher, refrigerator, electric stove.
- Television
- Small electrical appliances such as telephone, kitchen mixer, electric toothbrush, hair dryer
- Lights and lamps
- CD's
- Electric toy
- Alarm clock
- Cell phones
- Power strip with function indicators
- Batteries
- …
This list is not exhaustive, but is intended to provide an overview and create awareness of what all counts as electronic waste and must therefore be disposed of separately.
E-waste - facts & figures
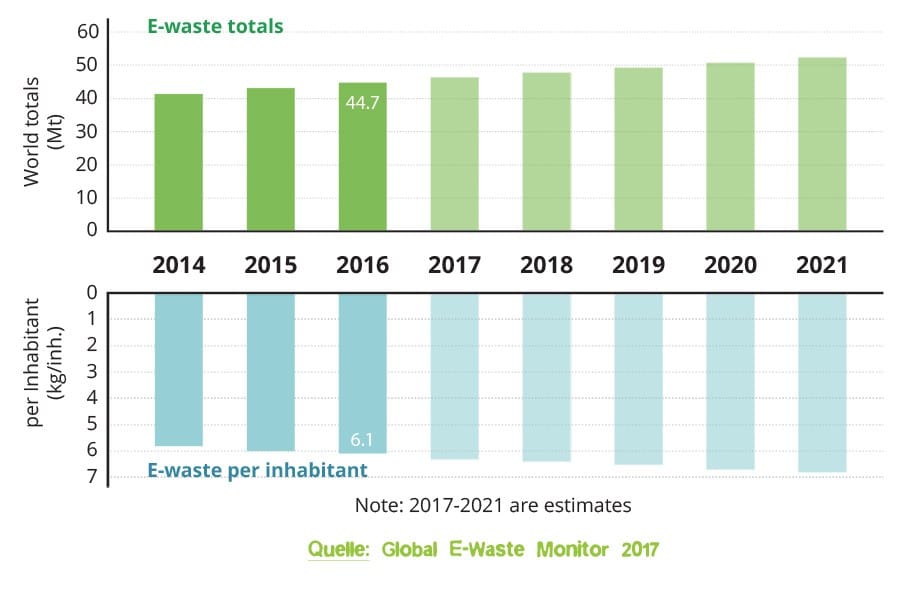
The following e-waste statistics₁, which were evaluated for 2016, show how big the e-waste problem really is worldwide:
Here's a little insight:
- Worldwide, a total of 44.7 million tons Electrical scrap to
- the global average is 6.1 kg per inhabitant
- Africa: 1.9 kg e-waste/inhabitant
- America: 11.6 kg e-waste/inhabitant
- Asia: 4.2 kg e-waste/inhabitant
- Europe: 16.6 kg e-waste/inhabitant
- Oceania: 17.3 kg e-waste/inhabitant
- Of the 44.7 million tons of electrical waste generated worldwide, only approx. 8.9 million tons recycled - that is just 20%
- China was again the country that produced the most e-waste in 2017 - viz. 7.2 million tons
- Germany also produced a total of around 1.9 million tons Electric waste. This is 5th place in the global ranking
- The Life cycle of a smartphone in Germany is only 19 months
- The estimated value of raw materials contained in the global generation of e-waste is as follows 55 trillion euros!
As you can see, the amount of e-waste per capita differs greatly from continent to continent. The following graph shows the development of the worldwide e-waste in million tons and per capita. Furthermore you can jump directly to the large infographic in the conclusion of the article with one click.
Disposing of electronic waste correctly - overview
Here you will find a quick overview of how you can dispose of your electrical waste. You can find more details such as the retailers' take-back obligation further down in the article.
Dispose of large electrical appliances
It goes without saying that you are not allowed to put large electrical appliances just anywhere. In addition, you could face a fine of up to 2,500 euros - and that's a good thing!
You can use your large old devices:
- Return to the dealer from whom you buy a new device
- Take to the recycling center (Wertstoffhof)
Dispose of small electrical appliances
Small electrical appliances are appliances whose longest edge is not longer than 25 cm.
You can also use your small electrical appliances:
- Hand in at certain dealers (for more information, see the section on the Electrical and Electronic Equipment Act)
- Take to the recycling center
Dispose of cell phones
Since a cell phone is a small electrical appliance, the same disposal options apply here, meaning you can:
- Take to the local recycling or materials center
- Deliver to an appropriate dealer
- There are also various ways to donate your old cell phone for a good cause. One place to start, for example, is Caritas.
Dispose of batteries
- You can also bring batteries to your recycling center
- Alternatively, a great many retailers have set up battery collection boxes where you can conveniently drop them in
Dispose lamps
Lamps - that is, illuminants such as energy-saving lamps and fluorescent tubes - must also be disposed of separately, as they contain toxic substances. You can dispose of these:
- bring to the recycling center
- in collection boxes for discarded light bulbs, which are now available at some retailers.
The same applies to LED lamps, although these do not contain toxic substances.
If you still have old light bulbs (!) at home, you can dispose of them in the normal household waste.
Small electrical appliances to the residual waste?
Whew! Can't I just throw my broken hair dryer in the residual waste? Or my kid's old flashing fire truck that doesn't work anymore? NO!
It is important to understand that even the smallest e-waste is hazardous waste and must be disposed of properly.
Electrical appliances - no matter how small - can contain toxic substances such as mercury, lead or cadmium. So if the old electrical appliances are not disposed of properly, all these substances end up in the environment.
Properly disposed of end-of-life devices can also be recycled, allowing precious metals contained in electronic waste to be recovered and reused.
Elektrogesetz - Are dealers obliged to accept electronic waste?
Everyone is probably familiar with the collection bins for old batteries, as these are located in very many stores. But other electronic waste can also be handed in at retailers.
How can I dispose of the old refrigerator?
How do I find the nearest drop-off location for my large waste appliances? In the case of large appliances such as old washing machines and old refrigerators, dealers are only obliged to accept the old appliance if they purchase an appliance that serves the same purpose.
In plain language, this means that the dealer from whom you buy a new washing machine must accept your old washing machine and, of course, dispose of it properly.
Obligation of certain dealers to accept small electrical appliances
For small electrical appliances, the obligation of certain dealers to take back applies regardless of whether one is a customer of the dealer or not. Small appliances are electrical and electronic equipment whose longest edge does not exceed 25 cm.
What many do not know: According to ElektroG, every retailer with a sales area of more than 400m² is obliged to take back small appliances in the retail store or in the immediate vicinity free of charge, irrespective of the purchase of an electrical or electronic appliance. The only restriction: The obligation to take back is limited to 5 old appliances per type. (§ 17 ElektroG)
You can find the collection and return points in your area at the ear foundation.
The previous option of handing in discarded appliances at recycling centers is still available. However, retailers, who are obligated to accept equipment, may not simply refer their customers to the recycling centers.
Is disposing of electrical appliances free of charge?
As already written above, the dealers who are obliged to accept old electrical and electronic equipment must accept it free of charge.
Then why do most online retailers charge to take the old equipment when you buy a new one? These costs are simply the cost of transportation. This also includes the cost of the service to carry the old electrical appliances from the house. The actual disposal of the device is free of charge.
There is also no charge for dropping off old appliances at recycling centers. Many municipal recycling centers even offer free collection of large old appliances such as washing machines and refrigerators. The small disadvantage here is that you have to put the appliance on the street yourself.

Recycling of electric waste in practice
Electronic waste must be disposed of separately from household waste. Not only because it contains harmful substances, but also because valuable metals are processed in it.
But how are the raw materials extracted from the scrap? First, the old devices have to be disassembled. Scrap metal such as circuit boards, cables and plugs can then be sold on. Special recyclers then melt down the scrap and extract the individual metals such as copper, gold, silver, zinc and aluminum.
Copper, for example, can be recycled to 100%, whereby recycling requires only half as much energy as extraction from ore. More difficult than the recovery of copper, aluminum, gold and the like is the recovery of rare earths such as lanthanum and yttrium, as these only occur in very small quantities in the products.
How can you avoid e-waste instead of disposing of it?
If your old device is broken, you should first check and consider whether you can (have) it repaired.
Unfortunately, repairs are sometimes disproportionately expensive - but the device doesn't necessarily have to end up on the electronic scrap heap. Just because you no longer need something doesn't mean that no one can do anything with it. Think of the Zero Waste Lifestyle. Before you dispose of your old equipment, please think for a moment if you can think of a way to reuse the equipment.
If your old device still works, offer it cheaply for sale or even to give away.
Even if your old electrical appliance doesn't work anymore, you can offer it for hobbyists. Why not use the old device as a spare parts store?
Here are some ideas of where you can sell or give away your old equipment:
- Local Facebook groups (For example, there are many "to give away" groups).
- Ebay Classifieds
- Flea market
- Social department store
- To the neighbor?
However, when reselling and re-gifting, it is enormously important to make it clear what condition the device is in. If the buyer is disappointed, no one has gained anything. Then proper disposal would actually be the better solution.
To avoid unnecessary electrical waste, you should also consider whether you really need this device before you buy it. Particularly with small children's toys, you will quickly realize after the initial consideration that you can invest the money much better elsewhere 😉.
Disposing of electronic waste - Actually simple, isn't it?
Basically, the disposal of old electrical appliances is not so complicated, often they are not even really broken. Out of the habit to get all things anytime and easily, we often choose the convenient way, just buy electrical appliances new and dispose of them the easiest way. I hope that this article has given you an overview of how to properly dispose of your e-waste.
Do you have any questions, suggestions or your own experiences on the subject of disposing of electronic waste? Then I look forward to your comment under this article.
Stay clean,

PS: Making less e-waste is part of a whole movement that is trying to make less waste. In the article Plasticfree lifestyle you learn how to avoid plastic waste.
PPS: The following infographic provides a good overview of the facts about e-waste and the correct disposal of electrical appliances.
References:
₁ https://www.itu.int/en/ITU-D/Climate-Change/Pages/Global-E-waste-Monitor-2017.aspx







Thanks for the tips and info on how to dispose of e-waste. My grandparents have accumulated a lot of scrap over the decades and never knew how to dispose of it. That's why I'm currently reading up on scrap metal trading and disposal.
Grateful for the tips on how to dispose of electrical appliances! We are getting ready to move, so something has to go. The problem arises with the energy saving lamps. I have heard of mercury, maybe then in the hazardous waste.
Moin Finn,
Exactly, energy-saving lamps contain the heavy metal mercury. This is toxic in high concentrations.
Just like fluorescent tubes and LED lamps, they must therefore be disposed of at separate collection points such as recycling centers.
Best regards
Christoph
Hello Anja,
in Hamburg, for example, there are many containers for small electrical appliances, which are distributed in the individual districts. Among other things, small electrical household appliances, such as electric toothbrushes, dry shavers, kettles, toasters, but also telephones, notebooks, keyboards, etc. fit into the containers.
Many greetings
Lina
Hi Lina,
exactly! Thanks for your tip :-)
Many greetings,
Christoph
In our city there is even a container to which you can bring your small electrical appliances scrap at any time. The container looks similar to a glass container with a flap like the old clothes containers. I am sure there is something like that in other cities as well.
Vg
Hi Christine, thank you so much for your comment! May I ask where you live? Such a container for old small electrical appliances is really a great thing and certainly contributes to the fact that hopefully soon all people dispose of their old appliances properly. I haven't seen such a container in my area yet, unfortunately....
Love greetings
Anja
Hello Christine,
That with the container I find quite practical, often it is small appliances such as a hairdryer, clippers or alarm clock what you want to dispose of in between.
Comments are closed.