The Climate Change and the global warming lead the list of biggest environmental problems of our time an. Even though slight fluctuations in the average temperature on Earth are not unusual, scientists have recorded an enormous increase since the 1960s. Today, one heat record is chasing the next in Germany, too - extreme weather such as droughts and floods are becoming more frequent.
In this article, I would like to give you everything you need to know about climate change. From facts about causes and consequences to solutions in everyday life.
Here is another short Table of contents about the article:
Notice: Global warming is an environmental problem that has thousands of causes and consequences, but also thousands of possible solutions. In this article, I have focused on the most important aspects. Feel free to comment below this post if you are missing something important.
What is climate change?
When people talk about climate change today, they are referring to man-made warming of the earth. The term Climate basically refers to the totality of weather conditions over a longer, meaningful period of time. For example, temperatures, precipitation, wind speeds or sunshine hours are measured and compared. In the case of global warming, a temperature increase of just 1-2°C can have serious consequences for people, animals and plants.
Greenhouse effect briefly explained
Global warming is basically caused by the so-called greenhouse effect. Short-wave radiation from the sun is sent to the earth, where it is converted into long-wave radiation and reflected back. However, the earth's atmosphere has a natural layer of carbon dioxide that reflects back some long-wave radiation and ensures that it is not freezing cold on earth. However, since the gases in the atmosphere have increased massively, we now speak of the man-made, so-called anthropogenic greenhouse effect. The following gases play a decisive role in this:
- Carbon dioxide (CO2) is the most common greenhouse gas produced by human activities and is responsible for about 63% of man-made climate change.₁ Each person is assigned a personal CO2 budget attributed.
- Methane (CH4) is responsible for about 19% of human-provoked global warming. It is emitted by cows, for example, and influences climate change about 25 times more severely than carbon dioxide.₂
- Nitrous oxide (N2O) is also referred to as nitrous oxide. Around 80% of nitrous oxide emissions in Germany come from agriculture. The greenhouse gas is around 300 times more harmful to the climate than carbon dioxide.₃
Facts, figures & statistics on climate change
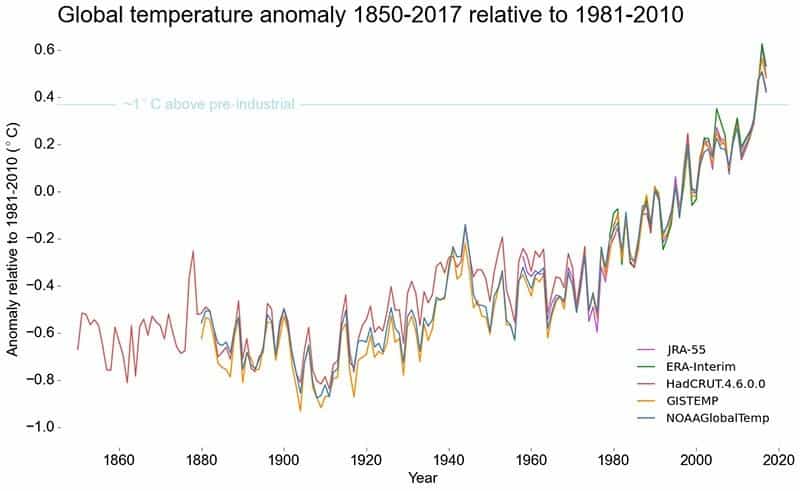
This graphic from the WMO₄ (World Meteorological Organization) impressively shows the alarming development of the average temperature on earth. Especially because this is a much-discussed scientific topic, it is important to be able to back up your own statements with figures. Here you can find some of the most important facts about global warming:
- According to NASA, 2017 was 0.90 ± 0.05 °C warmer than the mean over the period 1951-1980.₅
- Globally, the number of climate-related disasters has tripled since 1980.₆
- In 2016, the mean global near-surface air temperature was about 0.94°C higher than the 20th century mean.₇
- Since 1990, sea levels have risen by a global average of about 20 cm.₈
- Arctic sea ice is shrinking in its average annual extent by 2.7 percent per decade, and by as much as 7.4 percent per decade in summer.₉
At Climate facts.com you will find more important figures, data and statistics on global warming.
4 typical climate change myths
When the topic of global warming comes up in everyday conversations, it's not uncommon for typical myths surrounding the environmental problem to fly around your ears. Here I have listed four examples and also written a short but appropriate explanation.
"It's not getting warmer at all because we've had extreme cold spells."
It is true that we had a very cold winter in Germany in the winter of 2016. But please do not confuse the weather with the climate. The Weather refers to a physical state of the atmosphere at a particular time in a particular place. But with the term Climate means the statistics of the weather over a longer period of time, from which properties and changes can be derived.₁₀
"Climate change is just a conspiracy."
It is not surprising that there are many climate skeptics. Particularly as climate change evokes the need for social, economic and political change. Headwinds, of course, come primarily from the industries that are perceived to share the blame for climate change. However, 4014 studies exist on global warming, all of which were evaluated in 2013. 97% of the studies and 98% of the authors came to the conclusion that climate change is man-made.₁₁ The fact that the earth is warming is therefore most likely true.
"That the climate is changing is perfectly natural."
This myth is true in that the sun's radiation on the earth's surface creates a natural greenhouse effect. Volcanoes also spew massive amounts of CO2 into the atmosphere. But since the average temperature on earth has been increasing at a disproportionate rate, especially since the 1960s, the current global warming is anything but a natural process.
"A few degrees more or less won't make a difference."
Please do not make the mistake of equating the current temperature on your doorstep with the temperature used to assess global warming. For the latter, the global average temperature of the earth is always taken as a basis. Since the middle of the 20th century, the average global temperature has risen by about 1°C - the first consequences of this seemingly small change are being felt by us. increasing extreme weather events, such as droughts or floods already today..
With average temperatures starting at 2°C, up to 2 billion people worldwide are already affected by increasing Water Shortage affected. Up to 3 billion people are at risk from coastal flooding. In addition, infectious diseases are increasing dramatically and the biodiversity of animals and plants is decreasing drastically.₁₂
Causes of global warming

In addition to the natural causes of climate change, such as the radiation of the sun on the earth, the environmental problem has many man-made reasons. In the following, I would like to give you the most important ones.
Combustion of coal, oil and gas
Energy, heating and transportation - we burn coal, oil and gas for our lifestyle. But this can't go on forever, because fuels are in limited supply and the processes blow emissions into the atmosphere en masse. The greenhouse gases this creates prevent the sun's rays from being reflected back into space. This causes the temperature on Earth to rise, resulting in the consequences I'll explain in a moment.
Deforestation of rainforests
In 2017 alone, 29.4 million hectares of the world's forests, the size of the United Kingdom and Ireland, were deforested.₁₃ Approximately 80% of this forest loss is due to expanded agriculture for palm oil and soy, as well as timber and pulp plantations.₁₄
In the process, trees store the CO2 and contribute quite decisively to the fact that it is not even warmer on our earth. Through deforestation, the carbon dioxide escapes again and contributes to global warming. In addition, rainforests have an almost perfect water cycle that prevents the spread of deserts.₁₅
You can learn more about this in the separate article about the Environmental problem of deforestation.
Increasing livestock production due to rising demand for meat
According to the WWF, almost 70% of greenhouse gas emissions in Germany are attributable to animal products.₁₆ This is partly because cattle emit methane every minute - a greenhouse gas that drives the man-made greenhouse effect about 25 times faster than CO2. Worldwide, there are about 1.5 billion cattle alone, each emitting about 150 to 250 liters of methane per day.₁₇
In addition, (rain) forests are cut down for cattle pastures and feed production, and a total of around 15,500 liters of water are needed to produce one kilogram of beef. Water wastage and livestock farming are direct causes of climate change.
Poisoning, littering and overfishing of the oceans
Wastewater from industry and agriculture, Plastic waste in the environment and in addition the overacidification and Overfishing of the seas - It seems as if we don't care about the oceans. Yet they regulate the climate and store the gases we emit. Plankton, for example, is an excellent carbon dioxide reservoir.₁₈
Rapid growth of the world population
All the causes of climate change mentioned so far are also partly due to the disproportionate increasing world population to the world's population. Today, there are already 7.55 billion people living on our planet.₁₉ In 1980, there were still around 4.45 billion.₂₀ The number of people in the world has increased at a similar rate and disproportionately to the average temperature of the earth. This is not surprising, because every human being needs to eat, drink water and wear clothes. Every person consumes, and very few of them consciously sustainably.
Notice: We must not forget the Climate tipping pointssuch as the destruction of the Amazon rainforest. These "tipping points" can lead to a chain reaction that further accelerates climate change.
The consequences of climate change

In the end, global warming affects every living creature on this earth. But only one of them bears responsibility for it - humans.
The easiest way to visualize the consequences of climate change is to look at what happens on Earth at certain global average temperatures. These effects can be expected if the Earth warms as follows relative to the global average temperature in 1850 (about -0.4°C):
Up to 2°C:- Up to 1.7 billion people are affected by water scarcity.
- Increased coral bleaching due to increased ocean temperature
- More damage from floods and storms.
- Up to three million more people are at risk from coastal flooding.
- Increasing burden of infectious diseases, malnutrition, or heart disease
- Up to two billion people are affected by water scarcity.
- Up to 15 million more people are at risk of coastal flooding.
- Worldwide species extinction - especially in wetlands, forests and coral reefs.
- Up to 3.2 billion people are affected by increasing water scarcity.
These impacts are based on the information provided by the German Federal Environment Agency and the summary provided by NABU.₂₁
Here I would like to present the ecological, economic and social consequences of global warming once again in detail.
Effects on the environment

Man-made climate change has ecological impacts first and foremost, before it forces us humans to make changes. The following are some of the most important changes in our nature:
Ice Melt & Sea Level Rise
The increasing average global temperature is provoking an enormous loss of ice, which is particularly visible in Greenland. Since 2010, about 290 billion tons of ice per year have disappeared.₂₂
Melting ice will also further global warming, as sunlight will no longer be reflected by the light-colored ice but absorbed by the dark seawater.₂₃
The melting ice is causing sea levels to rise. Currently, it is rising at a rate of 0.3 cm per year.₂₄
First islands sink
The Fiji Islands east of Australia are the popular example of the consequences of climate change. The entire ecosystem of the islands suffers from storm surges and changes in rainfall. Even though many things have been changed locally on the islands to make them more sustainable, they are in danger of being submerged in a few years. The "Fischis" would then be among the first real victims of rising sea levels.₂₅
By the way: The higher the sea level rises, the more violent the effects of storm surges and the more saline the soil becomes.
Desolating landscapes & dying soils
Another consequence of global warming is a fundamental change in landscapes due to desiccated soils. Where deciduous forest grows and thrives now, soon only dwarf shrubs may grow.
According to a study by the French research center CNRS and Aix-Marseille Université, the Mediterranean region in particular is in danger of becoming deserted as soon as global warming reaches a plus of around 1.5°C.₂₆
Extreme weather & precipitation shift
We are already seeing an increase in droughts, storms and heavy rainfall. The calculation is basically quite simple: the more the temperature of the oceans rises due to climate change, the more water evaporates. The higher the air temperature, the more water is absorbed by clouds. The logical consequence is extreme weather and changes in precipitation patterns.₂₇ Longer periods of drought and the simultaneous scarcity of water are particularly extreme ecological effects of global warming.
Extinct animal and plant species
When lakes are drained, forests are cut down, oceans are overfished, and weather conditions change, wildlife and plants change as well. Habitats become smaller and they cannot adapt to the new conditions as quickly as we create them. As a result, thousands of animals and plants are threatened with extinction. The best example is the Polar bearwhich is visibly losing its habitat and food source due to the melting ice sheet and overfished seas. Due to the rising temperature of the seas as a result of climate change, there is also increased Coral Bleaching, a typical marine disease.
Impact on economy & society

As soon as the environment changes, changes naturally occur for us as well. Society and the economy are faced with major tasks. The following effects of global warming are already being felt today from an economic and social perspective.
Consequences of climate change for major sectors of the economy
The main costs of climate change are as follows.
- Costs due to direct consequential climate damage (e.g. due to high water)
- Adjustment costs (e.g. the raising of the dikes).
- Mitigation costs (e.g. investments in low-emission technologies).
On the Wiki education server these follow-up costs are explained in detail once again.
In particular, industries that depend on consistent temperatures and precipitation are already suffering greatly from global warming. These are for example Agriculture, forestry, energy and tourism.
Floods alone caused direct economic damage of over 90 billion euros between 1980 and 2011.₂₈
Health consequences of climate change
Global warming is already having a significant impact on our health around the world. The rise in temperature is promoting the spread of infectious diseases and allergies.₂₉ The number of heat-related deaths has also already increased, while the number of cold-related deaths has decreased.₃₀
Floods, droughts, forest fires, landslides, storms - extreme weather is taking its toll. Crop failures and drinking water shortages are no less severe. Fluctuations in food production in particular, made even more extreme by natural disasters, exacerbate the risk of the Famine.₃₁
Consequences for developing countries
The ecological consequences associated with man-made climate change particularly affect developing countries. The people in countries such as Sri Lanka, Fiji or Madagascar are mostly strongly dependent on the natural conditions in the environment. If the fish do not come, the fisheries are on the brink of extinction and the people are in famine. The same applies to crop failures due to extreme drought or flooding. In addition, developing countries usually do not have the necessary resources to prevent climate change, let alone to mitigate the consequences of climate change. This means that global warming is hitting the countries that can do least to prevent it.
Due to rising sea levels and other reasons for dwindling living conditions, moreover, 21.5 million people are already fleeing their homes.₃₂ This, in turn, is also giving rise to increasingly brutal, social conflicts, as can be observed in Germany.
Solutions against climate change

To halt global warming in the long term, consumers, business and politics must work together. There is no more room for greed or corruption. In this part of the article I would like to explain to you exactly what you can do in your everyday life against climate change and which tasks economy & politics have to solve now.
What everyone can do for the climate
In our Western society, an increasingly convenient way of life has crept in over the course of time - orders can be placed 24 hours a day via the Internet, for example, and are there the next day. You don't even have to leave the house to do it. This ingrained habit is one of the reasons why we have great opportunities in our everyday lives to counteract climate change in a very targeted way. Use the following Climate protection tips, to your Making everyday life more sustainable.
Eat vegan or just do without meat
Of course, you can also simply reduce your meat consumption - that's a valuable start. The example of giving up beef is a wonderful way to describe how you can bring about change through your everyday behavior. One kilogram of beef consumes a total of 15,500 liters of drinking water. You are counteracting the global shortage of drinking water. Tropical rainforests have to be cleared to grow animal feed such as soy. Soy meal is also imported and fed in Germany - you are therefore counteracting global deforestation. Since you are changing the demand for beef, fewer cows will have to be kept in Factory Farming are kept and there are generally fewer cows that emit methane. Consider meat again as a delicacy and not as an everyday meal. At best, give up meat altogether for a really big climate effect.
Tip: By eating a vegan diet, you can counteract so many environmental problems at once. Deforestation, climate change, water scarcity, species extinction... the list is basically endless. Just check out our text on the Start into a vegan life.
Buy regionally and seasonally
By eating regional and seasonal foods at your best plastic free shopping you are actively counteracting climate change. For example, avoid oranges from Spain because they are irrigated with groundwater, which causes the local water table to sink faster and threatens to dry out the regions. To produce one kilogram of oranges, 438 liters of water are used. In addition, energy-intensive transport is necessary, during which the fruit is usually chemically treated.₃₁
Tip: Read the article about regional shopping inspire a little bit.
Prefer the bicycle and public transport
According to the Federal Environment Agency, cars account for an average of 12% of annual CO2-emissions of Germans.₃₂ But in cities in particular, it is now possible to do without the car wonderfully - no more parking tickets, no more traffic jams, no more traffic lights. The alternative is public transportation such as buses and trains. To counteract climate change, you should also avoid domestic flights and take the train instead. Prices are still a bit more expensive these days, but that will change in the next few years due to societal pressure. Just try your best to travel emission-free - and if it has to be the car, try to organize carpooling. This will save you money and make other trips unnecessary.
Notice: Please also refrain from cruises. The ships are still allowed to use heavy oil and thus contribute significantly to climate change.
Switch to an eco-bank and green electricity
Did you know that it matters where you invest your money and what the origin of the electricity from your line is? You make the money in your accounts available to the banks - in return you receive interest. Many banks use the money to support nuclear energy or lignite companies. Therefore, it is better to invest your money in environmentally friendly, transparent banks. Here is a Eco banks comparison for you.
Electricity from hard coal or lignite or electricity from nuclear power plants is anything but climate-friendly. Nowadays, there are many suppliers of Green electricitythat generate their electricity exclusively from renewable sources such as wind, solar or hydroelectric power. You should give preference to these.
Save energy in the home
Green electricity is great, but it can be even more climate-friendly. In Germany, per capita electricity and heat consumption produces around 11 metric tons of CO2 ₃₃ You can also start here and reduce your personal energy consumption in the fight against climate change. Here are a few energy-saving tips for you:
- Do not use the air conditioner and rather ventilate in the morning and lower the shutters.
- Fill only as much water in the kettle as you need.
- Wash at 30°C without pre-wash - and air dry.
- Quickly close your refrigerator again
- Always boil water with a lid on the saucepan.
Do you have any other ideas? Then feel free to write a comment below this post.
What politics & business must do to combat climate change
Of course, it's great when consumers change their mindset on their own and, for example, give up meat or save energy in the household. But in order to accelerate the turnaround of our society, business and politics have a special obligation. The following measures must be implemented promptly:
- Complete coal phase-out by 2030 at the latest
- Intensive promotion of renewable energies
- Introduction of the CO2-tax (according to the Federal Environment Agency, one ton of CO2 long term 180€₃₄
- Reduction of public transport & rail costs
- Expansion of bicycle infrastructure in German cities
- Compliance with the objective of the Paris climate agreement
- Radical fight against illegal overexploitation (e.g. in the fishing or timber industry).
Do you have any other ideas? Then feel free to write a comment under this post.
Will global warming come to an end?

Yes - but the question is rather whether we can do it ourselves or whether nature will take over. We still have a realistic chance of stopping climate change. Since we are already feeling the damage of global warming, a rethink is finally taking place in society. It is important that we consumers and especially business and politics wake up from their deep sleep.
We have No environmental problem. We have a Society problem.
Prof. Dr. Maja Göpel, Secretary General of the Scientific Advisory Council of the Federal Government.
And for all the skeptics, even if we eventually find out that thousands of scientists from all over the world were wrong, we certainly won't be upset about clean rivers, the pleasant air, the decrease in the number of starving people, and the unique biodiversity on our planet, right?
Finally, I would like to give you four sustainable documentations on climate change, which you can watch on Netflix, for example:
- Before the Flood (the film depicts the consequences of global warming and shows honest reactions from world leaders).
- Chasing Coral (on the effects of climate change on the oceans).
- Cowspiracy (on the connection between meat consumption and climate change)
Do you have any questions, suggestions, or your own experiences with global warming that you'd like to share? Then feel free to write me a comment below this post. Thank you for sharing this article to convince as many people as possible to take active action against climate change.
Stay clean,

PS.: Take a look at our Environmental protection blog by. There you'll learn a lot more about the things we've done to the planet - but also how we'll solve the problems that have arisen.
References:
₁ https://ec.europa.eu/clima/change/causes_de
₂ https://www.wiwo.de/technologie/green/methan-wie-rinder-dem-klima-schaden/19575014.html
₃ https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/themen/boden-landwirtschaft/umweltbelastungen-der-landwirtschaft/lachgas-methan
₄ https://public.wmo.int/en/media/press-release/2017-set-be-top-three-hottest-years-record-breaking-extreme-weather
₅ https://scilogs.spektrum.de/klimalounge/verwirrspiel-um-die-absolute-globale-mitteltemperatur
₆,₁₁,₂₃ https://www.nationalgeographic.de/7-fakten-zum-klimawandel
₇ https://www.klimafakten.de/meldung/klimawandel-eine-faktenliste
₈ Prof. Dr. Karen Helen Wiltshire, Federal #Scientists4Future press conference, March 12, 2019.
₉ https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/themen/klima-energie/klimawandel/beobachteter-klimawandel
₁₀ https://www.mpimet.mpg.de/kommunikation/fragen-zu-klima-faq/was-ist-der-unterschied-zwischen-wetter-und-klima
₁₂ https://www.nabu.de/umwelt-und-ressourcen/klima-und-luft/klimawandel/11420.html
₁₃ https://blog.globalforestwatch.org/data-and-research/deforestation-is-accelerating-despite-mounting-efforts-to-protect-tropical-forests-what-are-we-doing-wrong
₁₄ https://blog.globalforestwatch.org/data-and-research/deforestation-is-accelerating-despite-mounting-efforts-to-protect-tropical-forests-what-are-we-doing-wrong
₁₅ https://www.abenteuer-regenwald.de/wissen/folgen
₁₆ https://www.wwf.de/themen-projekte/landwirtschaft/ernaehrung-konsum/fleisch/fleisch-frisst-land
₁₇ https://www.wiwo.de/technologie/green/methan-wie-rinder-dem-klima-schaden/19575014.html
₁₈ https://www.bpb.de/gesellschaft/umwelt/dossier-umwelt/61203/meere-und-klimawandel
₁₉ https://www.dsw.org/bevoelkerungswachstum-bis-2100
₂₀ https://de.wikipedia.org/wiki/Bevölkerungsentwicklung
₂₁ https://www.nabu.de/imperia/md/content/nabude/klimaschutz/ipccsynthese.pdf
₂₂ https://www.tagesspiegel.de/wissen/auswirkung-der-erderwaermung-groenlands-eisschmelze-beschleunigt-sich-massiv/24242822.html
₂₄ https://www.zdf.de/nachrichten/heute/steigt-das-meer-schneller-als-gedacht-100.html
₂₅ https://www.wwf.at/de/suedpazifik
₂₆ https://www.tagesspiegel.de/wissen/klimawandel-wueste-landschaft-rund-ums-mittelmeer/14749318.html
₂₇ https://www.greenpeace.de/themen/klimawandel/folgen-des-klimawandels)
₂₈ https://ec.europa.eu/clima/change/consequences_de
₂₉ Dr. Eckhart von Hirschhausen, Federal Press Conference #Scientists4Future, March 12, 2019.
₃₀ https://ec.europa.eu/clima/change/consequences_de
₃₁ https://www.welthungerhilfe.de/aktuelles/blog/ursachen-und-folgen-des-klimawandels
₃₂ https://www.greenpeace.de/themen/klimawandel/folgen-des-klimawandels
₃₁ https://www.naturfreunde.de/sites/default/files/attachments/nf_vw_methodenkoffer_leitfaden_final_website_1.pdf
₃₂ http://www.greentours.de/index.php/co2.html
₃₃ https://www.ews-schoenau.de/energiesparen/warum-energiesparen/klimaschutz
₃₄ https://www.umweltbundesamt.de/presse/pressemitteilungen/hohe-kosten-durch-unterlassenen-umweltschutz







Hello Christoph,
Thank you for your detailed contribution. I think you get to the heart of the causes of climate change. In my opinion, almost all of the causes can be broken down to a not inconsiderable extent to excessive livestock farming or agriculture. If we buy less animal products, this would have a positive effect on animal welfare, greenhouse gases, biodiversity (also in the rainforests) and plastic consumption.
Thanks again and best regards
Simon
Comments are closed.